Everything you need to know about Buffalo Fly
What is a Buffalo Fly?
A Buffalo Fly is a small 3-4 mm long blood-sucking fly with the scientific name Haematobia irritans exigua. It was introduced to Australia in 1825 via a shipment of Buffalo from East Timor.
-
What parts of Australia are Buffalo Fly found in?
Buffalo Fly are found across Northern Australia, from as far south as Taree in NSW, inland to Birdsville in Qld and as far south as Onslow in WA.
-
How long is a Buffalo Fly's lifecycle?
The Buffalo Fly life cycle is normally around 21 days, however, in hot humid conditions it can be as short as 14 days and when overwintering as long as 40 days.
Approximately 6 days of the cycle are spent as larvae feeding in the dung pats of cattle, and 7 days as pupae in the soil adjacent to the dung pat.
An adult female fly lays up to 12-15 egg batches in their lifetime. Each egg batch contains 2-25 eggs - with a potential total of 375 eggs per female.
-
How do Buffalo Fly feed?
Adult Buffalo Fly live permanently on their host animal and feed up to 40 times a day - taking a small amount of blood each time. Some animals can have as many as 5000 flies on them.
-
What effect do Buffalo Fly have on an animal's health?
Large numbers of flies feeding on an animal cause an increase in the animal's heart rate, respiration and urinary output.
The irritation from the flies can reduce the animal's feed intake resulting in significant weight loss. Australian studies show an increase in weight-gain of fly-free cattle of 20% compared to 8% over the same 4-month period.
The presence of Buffalo Fly on cattle can cause decreased milk production, devalued hides and the general unkempt appearance of infested animals.
-
What other concerns are there about Buffalo Fly?
As well as affecting weight-gain, Buffalo Fly can transmit a microfiliarial parasite (Stephanofilaria) from animal to animal. Lesions from this parasite can cause significant damage to cattle hides resulting in devalued returns to cattle producers.
-
What's the best way to deal with Buffalo Fly?
It is recommended to use an insecticidal ear tag management program that includes a rotation strategy. Both of these will reduce the likelihood of insecticidal resistance developing in the flies.
-
What is a fly tag management program?
A fly tag management program is a wider plan to help you combat flies and other pests.
We recommend the following;
- tag all the animals in a mob
- applying the recommended number of tags to each animal
- removing the tags at the end of the efficacy period
- adopting the fly tag rotation strategy
- synchronising your insecticide applications with your neighbours
-
What is a fly tag rotation strategy?
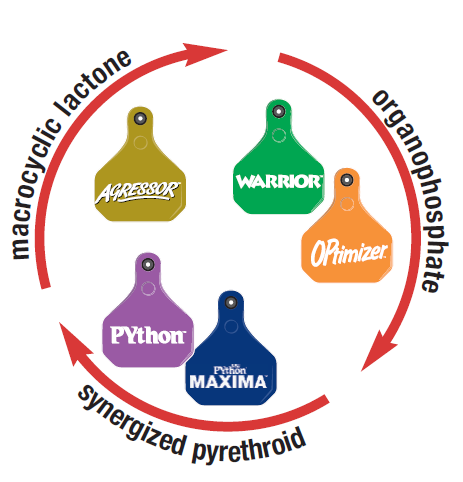
It is recommended to alternate insecticidal fly tags with differing chemical compounds to prevent over-exposure of a single chemical in the target insects. There is little or no cross-resistance between the major chemical classes.
Therefore fly tags containing three different insecticides are used in the rotation.
- AGRESSOR ear tag which contains Macrocyclic lactones.
- OPtimizer or WARRIOR ear tags which contain organophosphates
- PYthon or PYthon MAXIMA ear tags which contain synthetic pyrethroids